Introduction
Elasticsearch (http://www.elastic.co/products/elasticsearch) is an open-source distributed search engine built on top of Apache Lucene, a full-text search engine library. It is written in Java and uses Lucene internally for all of its indexing and searching, but it aims to make full-text search easy by hiding the complexities of the library behind a simple, coherent, RESTful API.
However, Elasticsearch is much more than just full-text search. It can also be described as the following:
- A distributed real-time document store where every field is indexed and searchable
- A distributed search engine with real-time analytics
- A product capable of scaling to hundreds of servers and petabytes of structured and unstructured data.
- A per-operation persistence - where document changes are recorded on multiple nodes within a cluster to minimize the chance of data loss.
Currently we use Elasticsearch (version 2.0.0) to facilitate a faster search of the resource data stored in SQL. The information is indexed as JSON documents, which follow a specific mapping (refer to the "Elasticsearch Mapping" section below).
Windows Elasticsearch Setup
Elasticsearch is built using Java, and requires at least Java 8 to run properly. The only requirement for installing Elasticsearch is a recent version of Java. Preferably, you should install the latest version of the Java which as of this writing is Java 8 update 45 or later.
Then set the location and version of Java to use by configuring the JAVA_HOME environment variable, for example:
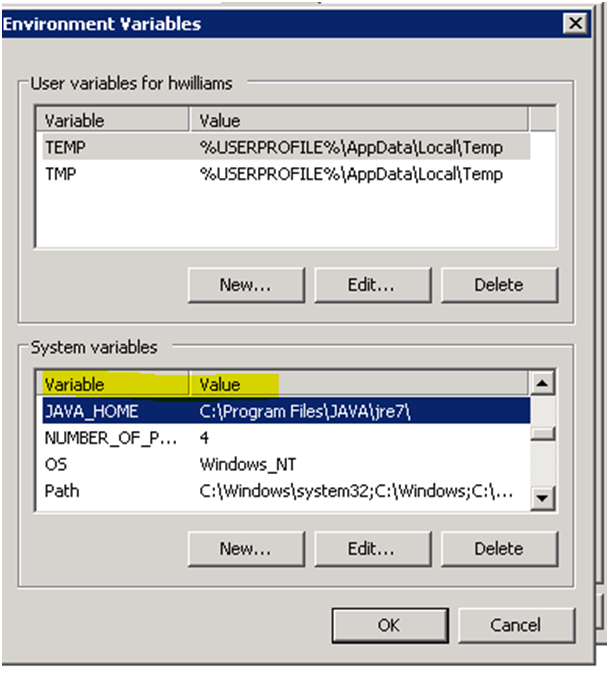
Afterwhich, download the latest version of Elasticsearch from http://www.elastic.co/downloads. To install, just download it and unpack it.
Directory Structure
| Directory |
Description |
| bin |
The scripts needed for running Elasticsearch instances and for plugin management |
| config |
The libraries used by Elasticsearch |
| lib |
Where all the libraries (such as Lucene) used by Elasticsearch are stored |
After Elasticsearch starts, it will create the following directories if they do not already exist.
| Directory |
Description |
| data |
Location where all the collection data used by Elasticsearch is stored |
| logs |
Files with information about events and errors that occur during the running of an instance |
| plugins |
The location for storing the installed plugins |
| work |
Temporary files |
Running Elasticsearch
Go to the "bin" directory and run Elasticsearch.bat from the command line. To test it, open another command prompt and run the command curl 'http://localhost:9200/?pretty'. You should see a response similar to the following:
{
"status" : 200,
"name" : "elaticsearch",
"version" : {
"number" : "1.5.0",
"build_hash" : " … ",
"build_timestamp" : " … ",
"build_snapshot" : false,
"lucene_version" : "4.10.4"
},
"tagline": "You Know, for Search”
}
Running Elasticsearch as a Service on Windows
This can be achieved through the “service.bat” script under the “bin” directory. With this script you can install, remove, manage or configure the service from the command line.
Usage: service.bat install | remove | start | stop | manager
Commands available are:
- install - Install Elasticsearch as a service.
- remove - Remove the installed service (and stop the service if started).
- start - Start the service
- stop - Stop the service
- manager - Start a GUI for managing the installed service.
Elasticsearch Mapping
Mapping is the process of defining how a document should be mapped to the search engine, including its searchable characteristics such as which fields are searchable and if/how they are tokenized. In Elasticsearch, an index may store documents of different "mapping types." Elasticsearch allows one to associate multiple mapping definitions for each mapping type. Explicit mapping is defined on an index/type level. By default, there isn't a need to define an explicit mapping, since one is automatically created and registered when a new type or new field is introduced (with no performance overhead) and have sensible defaults. Only when the defaults need to be be overridden must a mapping definition be provided.
Although Elasticsearch can manage documents without having to have a mapping defined for them, IOER runs Elasticsearch with a custom mapping because there are certain advantages in doing so. These advantages including:
- Being able to select which fields Elasticsearch searches and analyzes
- Stemming - reducing inflected and/or derived words to their word stem, base, or root form. For example, trains, training, and trained all have the same root word, "train." Many search engines treat words with the same stem as synonyms as a kind of query expansion, a process called conflation.
The Current Mapping
The Elasticsearch mapping used by IOER is currently as follows:
{
"settings" : {
"analysis" : {
"filter" : {
"special_character_splitter" : {
"type" : "word_delimiter",
"preserve_original" : "true"
}
},
"analyzer": {
"aggressive_ngram" : {
"tokenizer": "aggressive_ngram_tokenizer"
},
"td_analyzer" : {
"type": "custom",
"tokenizer" : "whitespace",
"filter" : [ "lowercase", "special_character_splitter" ]
}
},
"tokenizer" : {
"aggressive_ngram_tokenizer" : {
"type" : "edgeNGram",
"min_gram" : "2",
"max_gram" : "5",
"token_chars" : [ "letter", "digit" ]
}
}
}
},
"mappings": {
"resource": {
"properties": {
"ResourceId": { "type": "integer" },
"VersionId": { "type": "integer" },
"LrDocId": {"type": "string","index": "not_analyzed"},
"Title": {
"type": "multi_field",
"fields": {
"Title": { "type": "string", "store": "yes", "index": "analyzed", "analyzer": "td_analyzer" },
"English": { "type": "string", "store": "yes", "index": "analyzed", "analyzer": "english" },
"Ngram": { "type": "string", "store": "yes", "index": "analyzed", "analyzer": "aggressive_ngram" },
"Raw": {"type": "string", "index": "not_analyzed" }
}
},
"Description": {
"type": "multi_field",
"fields": {
"Description": {"type": "string", "store": "yes", "index": "analyzed", "analyzer": "td_analyzer"},
"English": { "type": "string", "store": "yes", "index": "analyzed", "analyzer": "english" },
"Ngram": { "type": "string", "store": "yes", "index": "analyzed", "analyzer": "aggressive_ngram" },
"Raw": {"type": "string", "index": "not_analyzed" }
}
},
"UrlTitle": { "type": "string", "index": "not_analyzed"},
"Url": {
"type": "multi_field",
"fields": {
"Url": { "type": "string", "store": "yes", "index": "analyzed", "analyzer": "td_analyzer"},
"Raw": { "type": "string", "index": "not_analyzed" }
}
},
"Requirements": {"type": "string"},
"ResourceCreated": {"type": "string","index": "not_analyzed"},
"Creator": {"type": "string", "index": "analyzed", "analyzer": "td_analyzer"},
"Submitter": {"type": "string", "index": "analyzed", "analyzer": "td_analyzer"},
"Publisher": {
"type": "multi_field",
"fields": {
"Publisher": { "type": "string", "store": "yes", "index": "analyzed", "analyzer": "td_analyzer"},
"English": { "type": "string", "store": "yes", "index": "analyzed", "analyzer": "english" },
"Ngram": { "type": "string", "store": "yes", "index": "analyzed", "analyzer": "aggressive_ngram" },
"Raw": { "type": "string", "index": "not_analyzed" }
}
},
"Keywords": {
"type": "multi_field",
"fields": {
"Keywords": { "type": "string", "store": "yes", "index": "analyzed", "analyzer": "td_analyzer"},
"English": { "type": "string", "store": "yes", "index": "analyzed", "analyzer": "english" },
"Ngram": { "type": "string", "store": "yes", "index": "analyzed", "analyzer": "aggressive_ngram" },
"Raw": { "type": "string", "index": "not_analyzed" }
}
},
"GradeAliases": { "type": "string", "index": "not_analyzed" },
"ThumbnailUrl": { "type": "string", "index": "not_analyzed" },
"LibraryIDs": { "type": "integer" },
"CollectionIDs": { "type": "integer" },
"IsleSectionIds": { "type": "integer" },
"StandardIds": { "type": "integer" },
"StandardNotations": {
"type": "multi_field",
"fields": {
"StandardNotations": { "type": "string", "store": "yes", "index": "analyzed", "analyzer": "td_analyzer"},
"Ngram": { "type": "string", "store": "yes", "index": "analyzed", "analyzer": "aggressive_ngram" },
"Raw": { "type": "string", "index": "not_analyzed" }
}
},
"UsageRightsUrl": { "type": "string", "index": "not_analyzed" },
"Paradata": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"Comments": {"type": "integer" },
"Favorites": {"type": "integer"},
"ResourceViews": { "type": "integer" },
"Likes": { "type": "integer" },
"Dislikes": { "type": "integer" },
"Evaluations": { "type" : "integer" },
"EvaluationsScore": { "type": "double" },
"Rating": { "type": "double" }
}
},
"Fields": {
"type": "nested",
"include_in_parent": true,
"properties": {
"Id": { "type": "integer" },
"Title": { "type": "string", "index": "not_analyzed" },
"Schema": { "type": "string", "index": "not_analyzed" },
"Ids": { "type": "integer" },
"Tags": {
"type": "multi_field",
"fields": {
"Tags": { "type": "string", "store": "yes", "index": "analyzed", "analyzer": "td_analyzer"},
"Raw": { "type": "string", "index": "not_analyzed" }
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}